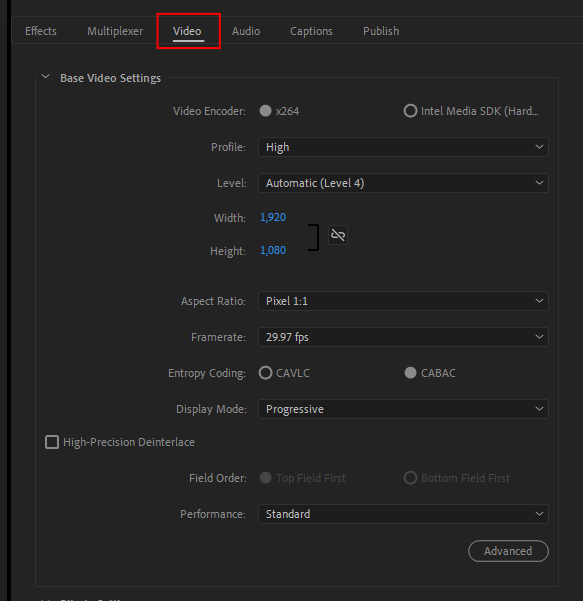
Allows altering the basic video settings from that of the Standard preset if necessary.
In Version 22.3 or later.
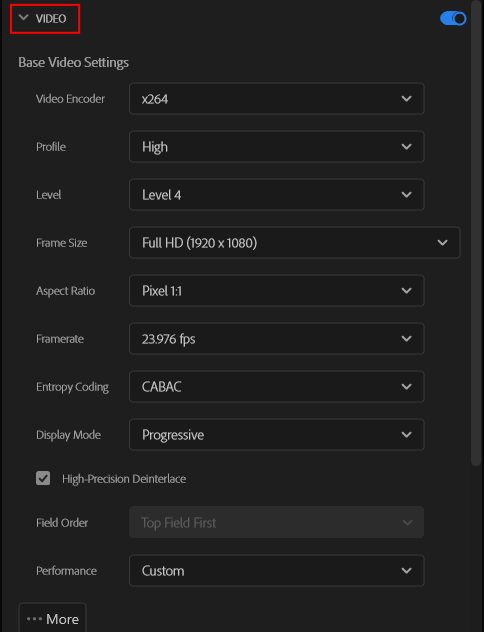
Basic Video Settings
When the proper environment is available, this setting allows you to select the [Intel Media SDK (Hardware)].
* Usable settings depend on the selected encoder.
The Baseline Profile is mainly for mobile device content encoding. The Main and High profiles allow advanced parameters such as CABAC and are mainly used for standard or high definition videos.
* In the Baseline profile, interlaced output is not allowed.
* When the Intel Media SDK Hardware encoder is set, the [Baseline], [Main] and [High] are available.
When set to Auto, a suitable level will be set automatically based on the other settings.
* Available settings are different depending on the selected video encoder.
* Level 4.2 and above, interlaced output is not allowed.
* When the Intel Media SDK Hardware encoder is set, the level is selectable between [High] and up to [5.2] .
The admissible values depend on the selected Profile & Level option.
* The value of the vertical resolution requires a multiple of 4 or multiple of 2. When the value is multiple of 2, interlaced output is not allowed. While it is possible to encode a picture larger than 1920 x 1080 (e.g., Level5.1 4096 x 2304 29.97 fps), such a size requires a tremendous amount of memory to encode. This increases the risk of having insufficient memory errors occurring while encoding the project. We recommend you set the image size within the Full High Definition size.
* Available settings are different depending on the selected video encoder.
When the display aspect ratio is selected, the outputted video will be played using the selected display aspect ratio regardless of the actual horizontal and vertical sizes. When the pixel aspect ratio is selected, the outputted video will be played using the specified horizontal and vertical sizes in square pixels.
* Available settings are different depending on the selected video encoder.
The admissible values depend on the selected Profile & Level and size option.
| CAVLC | Context-Adaptive Variable-Length Coding. A less efficient method of compression compared to CABAC, but requires less processing power, making it suited for low-spec decoders such as those found in mobile devices. |
| CABAC | Context-Adaptive Binary Arithmetic Coding. While this is the most efficient compression method available, it requires a tremendous amount of processing, both for encoding and decoding. Hence, this method is limited to Main and High profiles. |
| Progressive | Encodes in progressive mode (1 frame from video renders a complete picture on the display output). |
| Interlaced | Encodes in interlace mode (a mode used in TV broadcasting). When displayed on a computer monitor, horizontal scanlines may appear. |
| 3:2 Pulldown Playback | Used when 23.976 (24) fps video (anime, movies, etc.) is encoded as 29.97 fps video. Sets a flag indicating the player should apply 3:2 pulldown video processing during playback. |
| Progressive (2:2 Pulldown) |
Encodes at 29.97 fps in progressive mode, and sets a flag indicating the player should double the framerate at 60i to increase the encode efficiency. This option is only for 29.97 fps setting. |
This setting is available for Interlace display mode, and specifies which of the top or bottom fields is displayed first. Most players expect a top field first order, however some may require a bottom field first order. Refer to the player's requirements before changing this option.
With the Performance setting, increasing the picture quality priority level leads to a more detailed and precise analysis of the original picture, and makes the encoding engine's internal settings finer, resulting in an elevated picture quality. However, as the precision increases, the output speed decreases. Inversely, prioritizing the speed lowers the precision for the picture quality.
Available settings: Fastest, High speed, Fast, Somewhat fast, Normal, Somewhat slow, Slow, Very slow.
* When you set a different value than the preset in the Advanced Settings, the setting of the Performance displays [Custom].
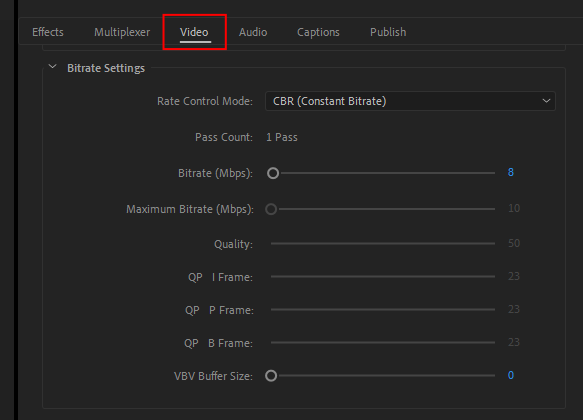
Bitrate Settings
In Version 22.3 or later, click the Video > [...More] button to display.
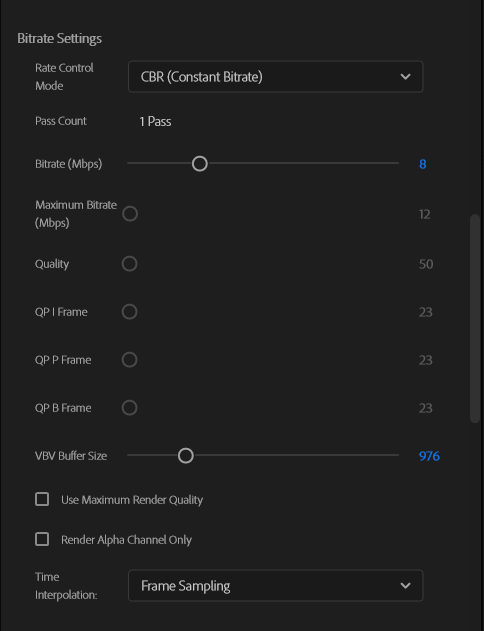
* There is no 2-Pass setting.
* In the x264 encoder, the pass count can be specified.
* Available only in the x264 encoder.
* Available only in the Intel Media SDK Hardware encoder.
* Available only in the Intel Media SDK Hardware encoder.
* Available only in the Intel Media SDK Hardware encoder.
* The Intel Media SDK Hardware cannot encode in VBR 2 pass.
Compared to the 2 pass VBR mode, the 1 pass mode can end up further from the target output size. If you need to keep the output file size closer to a given target size, use the 2 pass mode instead.
The default value is set as 0 (Automatic). When setting a size of 0 (Automatic), the actual VBV size is automatically calculated according to the video and bitrate characteristics. If you change the value, please set a suitable value for the device specification to playback.
* If it is not set in an appropriate value, there is a possibility that a device cannot play it, or encoding will require more time.
GOP Structure Settings
Specifies the MPEG data unit's GOP internal structure. GOP, or Group Of Pictures, is structured around I, P, and B frames, where an I frame is stand-alone and contains its entirely own description, and P and B frames are constructed on the difference between the I frame and themselves. Since the GOP is not only related to the picture quality or bitrate, but also strongly attached to the playback compatibility, you should exercise caution when editing its structure.
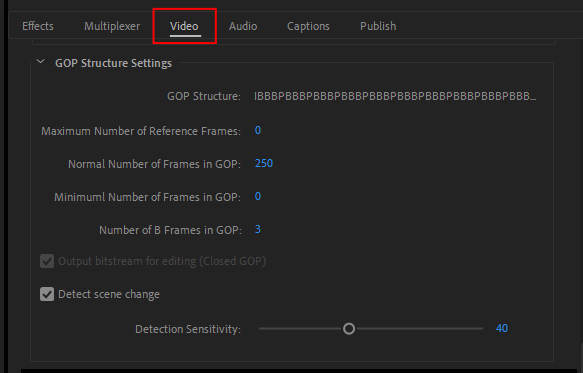
In Version 22.3 or later, click the Video > [...More] button to display.

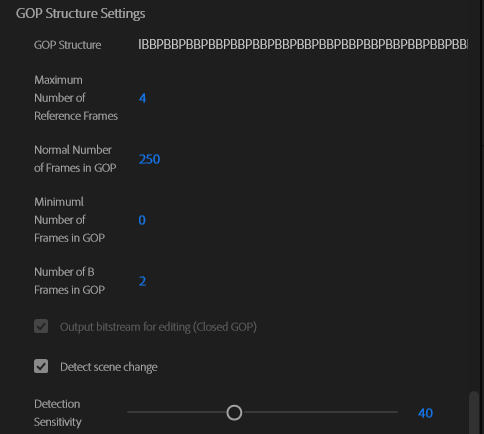
When using a B frame, the maximum number of reference frames must be greater than 1. By increasing the number of reference frames, you can improve the compression efficiency and output image quality. However, you also increase the memory usage during the encoding process, increase the encoding time, and may generate a file presenting compatibility issues with the player.
* When setting the value to "0", the value will be determined automatically.
* Cannot set a value higher than that of the Maximum Number of Frames in GOP.
* Cannot set a value other than that of the Normal Number of Frames in GOP.
* When set to "0" (Automatic), and the "VBV buffer size" setting is "0" (Automatic), the minimum number of frames is the lowest possible tenth of the "Normal Number of Frames in GOP" or the lowest possible "Framerate" setting.
Specifies the maximum number of B frames within a GOP between [0] to [16].
When set to "0", the encoder outputs only I frames. An I Frame only structure is for compressing data with very little motion; because there are no B frames, high-motion data compression efficiency is low, and the picture quality and bitrate do not match anymore.
* There is a possibility that a device cannot play a video which contains a lot of B frames in a GOP.
* When [MP4] is set in the [Stream Format:], this option is always enabled.
* This option is available only in the x264 encoder.
By detecting scene changes, you can improve the picture quality. When applied to a dynamic source where scene changes are numerous and the bitrate is set to a low level, the image quality may decrease. Since a scene change starts the generation of a new GOP, do not use this option when the player requires a fixed GOP length.
